Ethereum, the pioneering blockchain for smart contracts, faces scalability and centralization challenges as adoption grows. To address these issues, Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum’s co-founder, has proposed an innovative solution: partially stateless nodes.
This proposal aims to allow more users to run full nodes without requiring high-end hardware, thus contributing to a more decentralized and censorship-resistant network.
What Does "Stateless" Mean in Ethereum?
In the context of blockchain, "stateless" refers to a node’s ability to validate transactions without storing the blockchain’s entire state. Currently, Ethereum nodes must maintain a complete copy of the state, which demands significant storage and computing resources.Stateless nodes would allow users to verify transactions without storing all the data, reducing hardware requirements and making it easier to participate in the network.
Vitalik Buterin’s Proposal
Buterin has suggested implementing partially stateless nodes that store only a portion of the state relevant to the user, such as their balances and associated smart contracts. This would allow users to run full nodes on resource-limited devices like mobile phones or laptops. Additionally, this strategy would reduce dependence on centralized Remote Procedure Call (RPC) providers, mitigating censorship risks and improving the network’s resilience.
How Would a Partially Stateless Node Work?
A partially stateless node would efficiently validate blocks without storing the entire blockchain history. It would use cryptographic proofs to verify transactions and selectively keep parts of the state updated, based on the user's needs. For instance, a user interested only in their own balances and recent transactions could configure their node to store only that information, significantly reducing storage and bandwidth requirements.
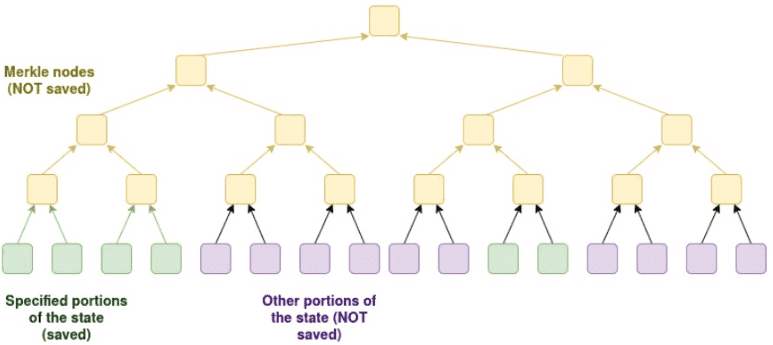
Benefits of This Solution
- Improved decentralization: By enabling more users to run full nodes, validation power is distributed, lowering the risk of centralized control.
- Greater privacy: Users can keep their personal data without relying on external service providers.
- Scalability: Reduced hardware requirements make Ethereum adoption more accessible across various devices.
- Censorship resistance: Less dependence on centralized RPC providers increases resilience against censorship attempts.
Challenges and Considerations
Although the proposal for partially stateless nodes offers significant advantages, it also presents technical challenges. Implementing efficient cryptographic proofs and managing partial state requires further research and development. Moreover, it’s crucial to ensure compatibility with existing applications and maintain the network's security.
The Future of Ethereum With Stateless Nodes
The transition toward partially stateless nodes is a major step toward a more scalable, decentralized, and resilient Ethereum network. While it’s still in the research and development phase, the proposal reflects the Ethereum community’s ongoing commitment to improvement and innovation. If successfully implemented, it could pave the way for broader Ethereum adoption and strengthen its position as the leading platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications.