Have you ever wondered why you need to send a photo holding your ID to buy Bitcoin? This requirement, known as KYC, is radically transforming the way we interact with the crypto world. Discover right now everything you need to know about this fundamental process.
Why do crypto platforms ask for your personal data?
KYC (Know Your Customer) is not simply a bureaucratic whim of exchanges. This procedure represents the meeting point between the revolutionary world of cryptocurrencies and the traditional global financial system.
As Gary Gensler, Chairman of the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission), points out: "Transparency in financial markets, including the crypto asset sector, is essential for investor protection and system stability."
Cryptocurrency platforms need to verify your identity for three main reasons:
- Prevent illegal activities such as money laundering
- Comply with international financial regulations
- Protect both the platform and its users from potential fraud
How the KYC process really works on crypto platforms
The KYC verification process in the cryptocurrency world follows a fairly standardized pattern, although it may vary slightly between different platforms. This procedure typically includes:
1. Collection of basic information: Full name, date of birth, nationality, and residential address.
2. Identity verification: Upload a photo of an official document (passport, ID card, or driver's license).
3. Proof of life: Many exchanges request a selfie or video where you hold your document next to a unique code or current date.
4. Proof of residence: Documents such as utility bills or bank statements that confirm your address.
5. Review and approval: The compliance team analyzes the documentation and approves or requests additional information.
This process can take from a few minutes to several days, depending on the platform and the complexity of your case.
Brian Armstrong, CEO of Coinbase, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges in the world, has commented: "While we understand that some users value anonymity, we've seen that implementing robust KYC processes has been key to building trust in the crypto ecosystem."
Who must comply with KYC verifications in the crypto world?
The obligation to undergo KYC verifications does not affect everyone equally in the cryptocurrency ecosystem:
- Centralized exchanges: Platforms like Binance, Coinbase, or Kraken require complete KYC for most of their services.
- DeFi platforms (Decentralized Finance): Many DeFi protocols do not require KYC due to their decentralized nature, although this is changing with new regulations.
- Brokers and custody services: Any service that acts as a financial intermediary is required to implement KYC.
- Stablecoin issuers: Companies like Circle (USDC) implement KYC for high-volume transactions.
However, as Charles Hoskinson, founder of Cardano, clarifies: "Truly decentralized applications operate through smart contracts where users interact directly with each other. These protocols, by definition, cannot impose KYC since there is no central intermediary."
The crucial difference between KYC and AML that you should know
Although often mentioned together, KYC and AML are distinct concepts with complementary purposes:
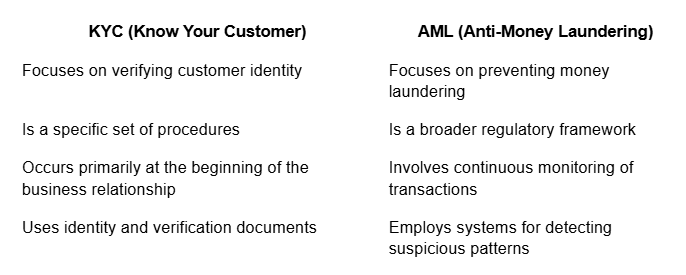
As Jesse Powell, co-founder of Kraken, explains: "KYC is simply a tool within the broader arsenal of AML regulations. It's like the difference between verifying who enters a bank (KYC) and monitoring what they do inside the bank (AML)."
Can users acquire crypto without undergoing KYC?
Yes, there are ways to acquire cryptocurrencies without going through KYC processes, although with important limitations:
- P2P exchanges (peer-to-peer): Platforms like LocalBitcoins or Hodl Hodl allow direct transactions between users.
- Bitcoin ATMs: Some cryptocurrency ATMs allow small purchases without verification.
- DEX (Decentralized Exchanges): Platforms like Uniswap allow exchanges without KYC, but you'll need initial cryptocurrencies to operate.
- Mining: Generating cryptocurrencies through mining doesn't require KYC, although it involves a significant investment. How to mine Bitcoin or Ethereum.
However, Andreas Antonopoulos, a renowned Bitcoin educator, warns: "KYC-free access to cryptocurrencies is increasingly difficult. Although options exist, most on-ramps from fiat currencies require some form of identity verification."
It's important to note that acquiring cryptocurrencies without KYC can significantly limit your options for later converting them to traditional money.
The historical origin of KYC regulations in finance and cryptocurrencies
KYC regulations weren't born with cryptocurrencies, but have a long history in the financial system:
- 1970: The Bank Secrecy Act is approved in the U.S., establishing the first foundations for monitoring financial transactions.
- 1989: Creation of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), which establishes global standards against money laundering.
- 2001: After the September 11 attacks, the U.S. PATRIOT Act drastically strengthens KYC requirements.
- 2013-2014: The first major Bitcoin exchanges begin implementing KYC policies after regulatory pressure.
- 2018: The EU's Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directive comes into force, explicitly including cryptocurrencies.
Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum, has reflected on this evolution: "The tension between financial transparency and personal privacy is one of the great debates of our era. KYC regulations are the battlefield where this discussion is fought."
Advantages and disadvantages of KYC in the crypto ecosystem
Advantages
- Increased security: Reduces the risk of fraud and protects legitimate users.
- Regulatory legitimacy: Facilitates institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies.
- Legal protection: Verified users have greater legal backing in case of disputes.
- Higher transaction limits: Verified accounts usually have greater operational capabilities.
Disadvantages
- Privacy compromise: Contradicts the principle of anonymity in cryptocurrencies.
- Risk of data breaches: Personal information may be vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- Inclusion barriers: Excludes people without standard documentation or fixed address.
- Operational costs: Makes crypto platform services more expensive.
Elizabeth Stark, co-founder of Lightning Labs, summarizes this duality: "The balance between privacy and regulatory compliance is the great challenge of the crypto sector. We need to find solutions that protect users without stifling innovation."
What happens to your personal information after KYC verification?
One of the biggest concerns for crypto users is the fate of their personal data after completing the KYC process:
1. Secure storage: Regulated platforms must store your information in encrypted and protected databases.
2. Use for monitoring: Your data is used to analyze transaction patterns and detect unusual activities.
3. Mandatory retention: By law, companies must retain this information for several years (generally 5-7 years).
4. Limited sharing: In certain cases, your data may be shared with:
- Regulatory authorities during investigations
- Other financial institutions for cross-verification
- External identity verification services
Michael Saylor, founder of MicroStrategy and prominent Bitcoin investor, opines: "Absolute financial privacy and effective regulation are competing goals. The challenge is finding the balance that allows innovation while protecting the system against abuse."
Ethereum ETFs and the impact of KYC on institutional investments
The recent approval of Ethereum ETFs has marked a milestone in the institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies, where KYC plays a fundamental role:
Ethereum ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) allow traditional investors to gain exposure to this cryptocurrency without needing to directly manage digital assets. Funds offered by companies like BlackRock, Fidelity, and Grayscale represent a regulated and verified gateway to the crypto world.
For institutional investors, robust KYC verifications are a competitive advantage, as they:
- Ensure regulatory compliance
- Reduce operational and legal risks
- Facilitate audits and financial reporting
Raoul Pal, former Goldman Sachs executive and founder of Real Vision, explains: "The KYC/AML infrastructure is precisely what has allowed large institutional capital to begin flowing into the crypto ecosystem. Without these guarantees, we simply couldn't see the participation of pension funds or traditional asset managers."
The future of KYC in an evolving crypto world
KYC in cryptocurrencies represents the meeting point between the original vision of a decentralized financial system and the practical needs of regulation in a global economy. Although it may seem contradictory to some fundamental principles of cryptocurrencies, its implementation has been key to institutional adoption and legitimization of the sector.
In the words of Sheila Warren, Director of the Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the World Economic Forum: "The real challenge isn't eliminating KYC, but reimagining it for the digital age. We need solutions that respect privacy while allowing the verification necessary for a secure financial system."
As technologies evolve, we can expect innovations such as decentralized identity verifications and Zero-Knowledge Proof systems that could radically transform the way KYC is implemented, better reconciling privacy and compliance.
What is undeniable is that, at least for now, KYC will continue to be a fundamental part of the crypto ecosystem, especially at the entry and exit points to and from the traditional financial system.
